In the field of metal forming, selecting the right mold is essential to ensure efficient production, consistent quality, and cost-effectiveness. Among the most widely used options are the Progressive Stamping Mold and the transfer mold. Both methods serve the purpose of shaping and producing metal parts, but they differ in design, operation, and applications. Understanding these differences helps manufacturers decide which option suits their production needs best.
What Is a Progressive Stamping Mold?
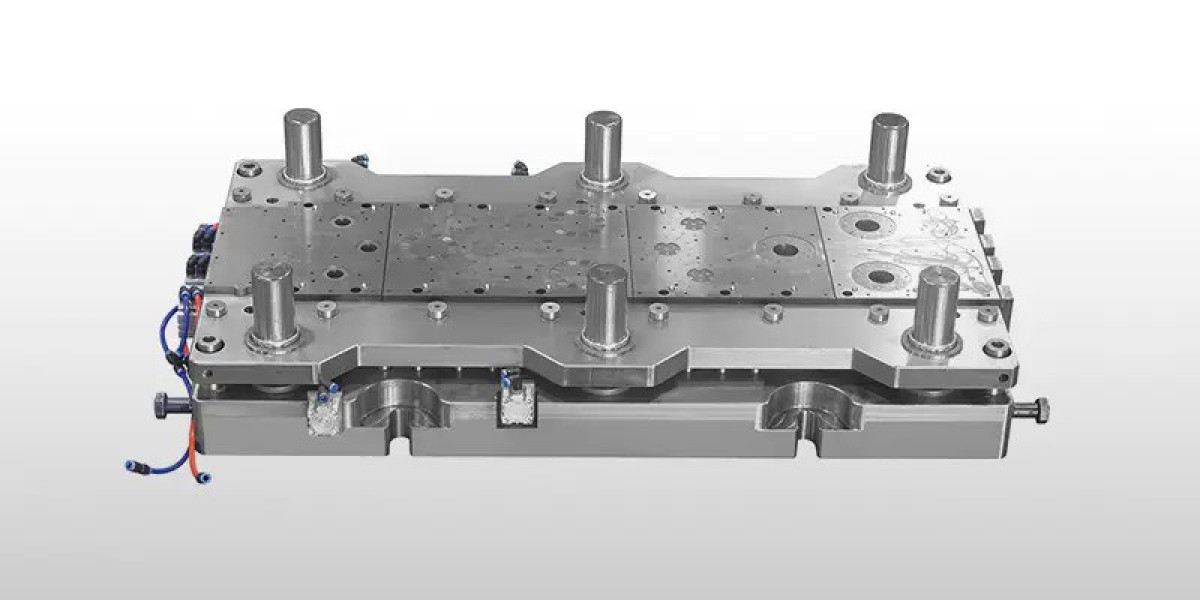
A Progressive Stamping Mold is designed to perform multiple operations on a strip of metal as it advances through a press. Each station in the mold completes a different step, such as punching, bending, or forming. By the time the strip reaches the final stage, a finished part is separated from the material.
The main advantage of a Progressive Stamping Mold is its efficiency. It allows manufacturers to produce large volumes of small to medium-sized components with consistent quality. Additionally, material utilization is typically higher because the process is optimized to reduce waste.
What Is a Transfer Mold?
A transfer mold, on the other hand, works by moving individual pieces of metal from one station to another. At each station, a different operation is performed, but instead of being carried along a strip, the part is transferred mechanically or with a robotic system.
This method offers flexibility in handling larger or more complex parts that may not be suitable for a Progressive Stamping Mold. Since each piece is worked on individually, transfer molds can manage parts that require deep drawing or multiple forming steps.
| Comprehensive life: | ≥160 million punches |
| Blade die life: | ≥5 million strokes/0.1mm |
| Mold structure: | Three-plate mold base + ball guide |
| Effective cutting edge height: | ≥8mm |
| Blade material: | DJ40 |
| Grooved die form: | Punch grooved die, slow wire finishing, the punch is polished using a special process to remove the oxidation layer |
| Guide parts: | Precision + high hardness |
| Blanking speed during running-in period: | 80-280 punches/minute |
| Blanking speed: | 280-300 punches/minute |
| Concentricity: | ≦0.05mm |
| Protection device: | Equipped with misfeed protection device |
| Punching burr: | ≦0.05mm |
| Riveting force: | 30N |
| Safety device: | Misfeed detection + equal height limit column |
| Product output form: | Conveyor belt Rotor control device Chute control device |
| Plate control device: | Cylinder |
| Mold base material: | Upper and lower mold seats P20. middle unloading seat P20. the second and fourth levels are made on the same set of molds and are interchangeable during production. The shaft hole can be used for three interchangeable pumping plates. |
| Spare parts provided: | 30% of wearing parts |
| Internal plate material: | Cr12MOV |