Phosphate ions, essential for a variety of industrial and agricultural applications, are widely used in products such as fertilizers, detergents, and food additives. As a vital compound in various sectors, the demand for phosphate ions has seen consistent growth, driven by the increasing global need for agricultural productivity, environmental conservation, and chemical innovations. Establishing a manufacturing plant dedicated to phosphate ion production can be a profitable venture, but it requires careful planning and execution. This project report outlines the key factors to consider when setting up a phosphate ion manufacturing plant, including the production process, required materials, equipment, and market potential.
Understanding the Role of Phosphate Ions
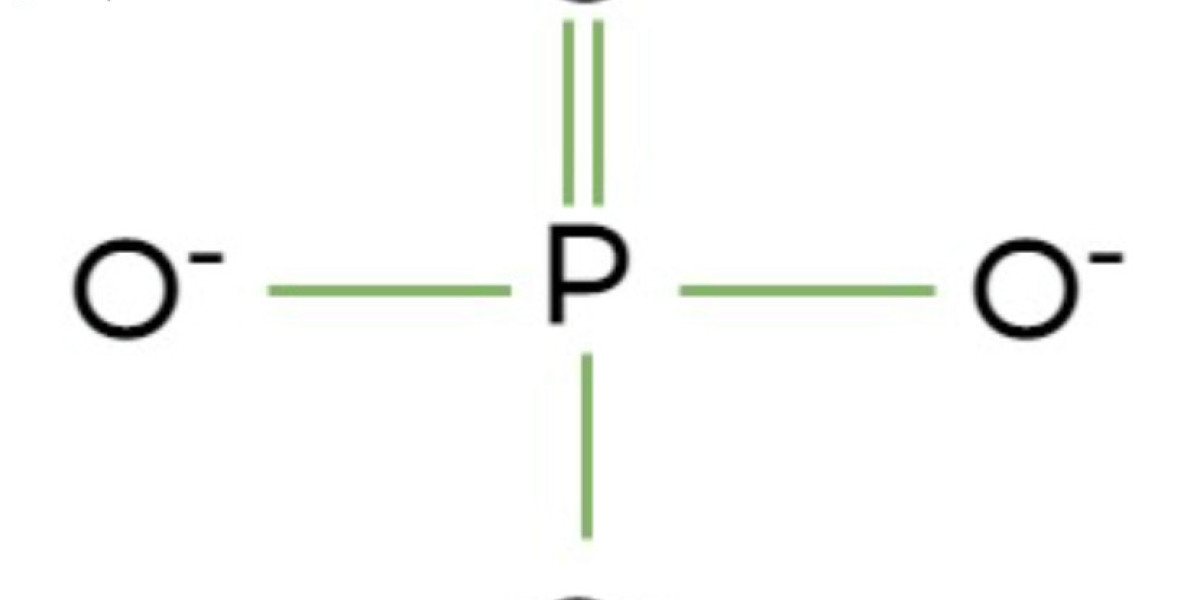
Phosphate ions (PO₄³⁻) are fundamental in numerous applications due to their chemical properties and versatility. They play an integral role in biological systems, such as the formation of DNA, RNA, and cellular energy storage molecules like ATP. In addition to their biological importance, phosphate ions are a key component in various industrial processes.
a. Agricultural Use: Fertilizers
The most significant application of phosphate ions is in fertilizers. Phosphates are vital for plant growth, influencing root development, flowering, and fruiting. Phosphate-based fertilizers are widely used to enhance soil fertility and increase crop yields, making them essential for the agricultural industry.
b. Food and Beverage Industry
In the food industry, phosphate ions are used as food additives, providing a range of functions such as acting as emulsifiers, leavening agents, and stabilizers. They help preserve the freshness of packaged food products and enhance the texture of processed meats, cheeses, and soft drinks.
c. Detergents and Cleaning Products
Phosphates are used in detergents and cleaning products for their ability to soften water, enhance cleaning power, and break down grease. However, environmental concerns over phosphates’ contribution to water pollution have led to efforts to reduce their use in household cleaning products in certain regions.
d. Water Treatment and Industrial Applications
Phosphate ions are also utilized in water treatment processes to prevent the corrosion of pipes and boilers. Additionally, they are employed in various industrial applications such as metal treatment, flame retardants, and the manufacturing of certain chemicals.
With such broad applications, the demand for phosphate ions is high, particularly in regions with substantial agricultural activity and growing industrial needs.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@ https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/prefeasibility-reports/phosphate-ion-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Key Factors to Consider When Setting Up a Phosphate Ion Manufacturing Plant
Setting up a phosphate ion manufacturing plant requires significant investment in infrastructure, machinery, and resources. Below are some critical considerations that will help ensure the success of the plant:
a. Location Selection
Choosing the right location for the manufacturing plant is crucial. Factors to consider include:
Proximity to Raw Materials: Phosphate rock, which is the primary raw material for phosphate ion production, must be readily available. Locations near major phosphate mining regions or suppliers will reduce transportation costs and improve production efficiency.
Access to Markets: The plant should be situated near key markets, including agricultural hubs, food manufacturers, and industrial areas, to reduce logistics costs and improve the speed of distribution.
Transportation Infrastructure: Accessibility to highways, ports, and railways will facilitate the transportation of raw materials and finished products. Having easy access to major transport routes is vital for both local and international distribution.
Energy and Water Availability: Phosphate ion production requires significant energy for chemical processes and water for cooling. Ensuring that the location has reliable access to these utilities is essential for smooth plant operations.
b. Raw Material Sourcing
The primary raw material for phosphate ion production is phosphate rock. This naturally occurring mineral is rich in phosphate compounds and is mined in various parts of the world, including Morocco, China, and the United States. Ensuring a steady and cost-effective supply of high-quality phosphate rock is vital for maintaining continuous production.
Other materials required for the production process include chemicals like sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid, which are used in the conversion of phosphate rock into soluble phosphate forms.
c. Equipment and Technology Requirements
The equipment and technologies used in the phosphate ion production process play a significant role in the efficiency and scalability of the manufacturing plant. Key equipment includes:
Crushing and Grinding Machines: Phosphate rock needs to be crushed and ground into a fine powder before further processing. Crushing and grinding machines break the rock down into smaller particles to make it more accessible for chemical treatment.
Chemical Reactors: Reactors are used for the conversion of phosphate rock into phosphoric acid or other phosphate derivatives. The reactors need to be capable of handling the high temperatures and pressures involved in the process.
Filtration and Separation Systems: These are used to separate impurities from the phosphoric acid solution or other by-products during the manufacturing process.
Dryers and Kilns: In some processes, the produced phosphate compound is dried or calcined using high-temperature kilns or dryers.
Packaging and Storage Systems: Once the phosphate ions are produced, they need to be packaged for distribution. Automated packaging systems help to efficiently package the product in various sizes for consumer or industrial use.
d. Workforce and Operational Requirements
A phosphate ion manufacturing plant requires skilled labor to operate the machinery, manage production processes, and maintain quality control. Some key workforce roles include:
Plant Operators: These workers will operate and monitor equipment throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring the plant runs smoothly.
Maintenance Technicians: These individuals are responsible for ensuring that the plant’s equipment is regularly maintained and in good working order to prevent production delays.
Quality Control Technicians: Quality control is vital to ensure the purity and consistency of the final product. Technicians will conduct regular tests on raw materials and finished products.
Logistics and Distribution Staff: Workers responsible for handling, packaging, and distributing the finished product will be needed to ensure the efficient flow of goods to market.
e. Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Impact
Compliance with local and international regulations regarding safety, environmental impact, and health standards is essential for the smooth operation of the plant. These regulations include:
Health and Safety Standards: Ensuring the safety of workers and minimizing risks associated with hazardous chemicals and machinery is critical. The plant must implement safety protocols, emergency response plans, and regular training for employees.
Environmental Regulations: The production of phosphate ions can result in the generation of waste materials and pollutants. The plant must have systems in place for waste treatment, emissions control, and recycling to reduce its environmental footprint.
Quality and Food Safety Standards: For products used in food applications, compliance with food safety standards is necessary to ensure the product is safe for consumption. Certifications such as ISO 22000 or HACCP may be required for food-grade phosphate ion production.
Phosphate Ion Production Process
The production process for phosphate ions generally involves several key stages, each of which requires specialized equipment and expertise. The following is a typical outline of the process:
a. Mining and Preparation of Phosphate Rock
The first step in the production of phosphate ions is the extraction of phosphate rock from mining operations. Once mined, the rock is crushed and ground into fine particles to facilitate the chemical treatment process.
b. Chemical Treatment to Produce Phosphoric Acid
Phosphate rock is typically treated with sulfuric acid to produce phosphoric acid, which is a soluble form of phosphate. This reaction dissolves the phosphate in the rock, allowing it to be processed further.
c. Purification and Filtration
The phosphoric acid solution is then purified to remove impurities that may interfere with its quality. This is done through a series of filtration and separation processes, which ensure that only high-quality phosphoric acid is produced.
d. Conversion to Phosphate Ions
Once purified, the phosphoric acid can be further processed to create phosphate ions. This may involve neutralization or other chemical treatments depending on the intended application of the product.
e. Drying and Packaging
The final product, which is typically a powder or granule form of phosphate ions, is then dried using specialized dryers or kilns to remove excess moisture. After drying, the phosphate ions are packaged for shipment and distribution.
Market Trends and Demand for Phosphate Ions
The market for phosphate ions is influenced by several factors, including the agricultural sector’s growth, increasing demand for plant-based food additives, and industrial use in detergents and water treatment. The following trends are shaping the market for phosphate ions:
Global Population Growth and Agricultural Needs: As the global population increases, the demand for food production rises. Phosphate fertilizers are essential for ensuring agricultural productivity, which supports the continued demand for phosphate ions.
Environmental Awareness and Sustainability: As concerns over environmental degradation grow, there is increasing pressure on industries to minimize the environmental impact of phosphate production. Innovations in sustainable phosphate production methods and recycling technologies are expected to shape the future of the industry.
Technological Advancements: Ongoing research and development in phosphate production technologies are helping to improve the efficiency of manufacturing processes, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impacts.
Setting up a phosphate ion manufacturing plant presents an exciting opportunity to tap into a market with diverse and growing applications. By carefully considering factors such as location, raw material sourcing, equipment, workforce needs, and regulatory compliance, businesses can ensure the success of the plant while meeting the rising demand for phosphate ions in agriculture, food production, and industrial sectors.